 |
AutoFEM Analysis Types of Finite-Element Model | ||||||
Types of Finite-Element Model
Depending on geometric features of the analysed structure, in the AutoFEM Analysis it is possible to construct any of two kinds of finite-element models:
| • | volumetric finite-element model, based on tetrahedral finite elements; |
| • | shell finite-element model, based on triangular finite elements. |
Let us consider the cases of using each type of the finite element meshes in detail.
Tetrahedral finite-element model. In this case, to approximate geometry of the modeled part, its representation by finite elements of tetrahedral shape is used. Tetrahedral finite element mesh well approximates the arbitrarily complex shape of parts and provides satisfactory results of modelling physical problems for objects of arbitrary shape, whose characteristic sizes along three space dimensions (length, width, height) are comparable with each other. Most parts and joints of the standard mechanical and instrumental engineering equipment fall into this category.
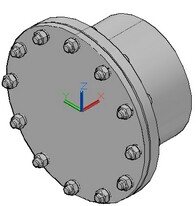
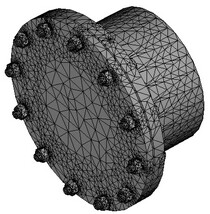
Volumetric 3D model of a structure and its representation using tetrahedral finite elements
Shell finite element model. Substantial class of structures used in people’s life has a special geometric shape when one of the dimensions (thickness) is considerably smaller than two other dimensions – width and length. Such structures are usually called thin-walled. For example, in mechanical engineering these structures can serve as the shells of various machines, spiral of turbines; in instrumental engineering – flexible elastic elements: accordion boots, membranes, including crimp, plate springs; in civil engineering – coatings, floors, ramps, sheds and aprons, in shipbuilding – hulls of ships; in aircraft industry – fuselage and wings of aircrafts; in industry – various tanks: cisterns, reservoirs, etc.

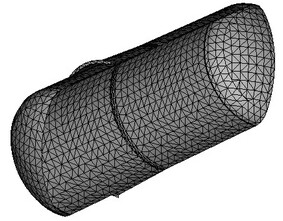
Thin-walled structure and its representation using triangular finite-elements
For finite element analysis of thin-walled structures, instead of tetrahedral elements, it is possible to use laminar (shell) finite elements that allow the user to obtain a satisfactory solution with smaller computational effort than when using three-dimensional finite elements.