 |
AutoFEM Analysis Thermal Analysis Settings | ||||||
Thermal Analysis Processor Settings
On the [General] tab, you can define or edit the descriptive attributes of the current study, as the name or a comment.
The [Solve] tab contains settings for solving systems of algebraic equations, with their meanings similar to the settings of the «Static analysis» study (see the respective section). Note that the «Calculate using linear element» mode can be used in most cases of thermal analysis, facilitating much faster calculations. Unlike studies in Statics, Frequency analysis and Buckling, results of temperature distribution over the model's volume achieved under the linear interpolation assumption are not much different from the respective results obtained from using a quadratic interpolation.
Before starting calculations, on the tab [Parameters] the user can indicate the type of solved thermal analysis problem: stationary (steady state mode) or non-stationary thermal conduction (transient process).
For non-stationary thermal conduction, it is necessary to specify a process duration («Total process time»), time step and initial temperature.
In the thermal analysis, controls «Initial temperature|Use preset temperature» allow the user to define as an initial temperature:
• |
initial temperature prescribed with the help of the command "AutoFEM | Loads/Restraints | Initial Temperature..."; |
• |
the default value of temperature at those finite element nodes where the initial temperature was not defined by the user. |
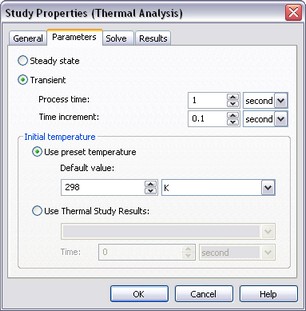
«Parameters» tab of the thermal analysis study parameters window
The «Use heat-task results» control allows defining the initial temperature by the results of an earlier conducted thermal analysis. This dialogue item becomes accessible to the user, if there are earlier conducted thermal studies present in the model. In the drop-down list select the name of a solved thermal analysis study and, if necessary, the time instant, to which the solution pertains. Please note that certain conditions are to be met for using thermal analysis results as the initial temperature conditions:
1. Identity condition of finite element meshes in both thermal analyses. The simplest way of achieving such identity is the use of the "Copy" command available in the context menu. The sequence of steps can be, for example, as follows:
a) create a study of the "Thermal Analysis" type, generate a mesh, define boundary conditions, and run. We assume that the solved temperatures will be used for defining initial temperatures in another study of the transient thermal analysis;
b) create a study's copy using the «Copy» command;
c) define boundary conditions of a transient study in thermal analysis. On the «Parameters» tab of the study's properties, select the name of the first study and, if that's a transient analysis, the desired time step.
As a result, we have two studies of different types, but with identical finite element meshes.
2. The "Calculate using linear element" property on the "Solve" tab of the study parameters dialogue should use the same settings in both studies. For example, if the first thermal analysis is done by linear elements, then the second thermal analysis based on the former thermal analysis results can also be run only by linear elements.
Note also that solving a transient heat transfer study requires more CPU time as compared to the steady state heat transfer, since in the former case the systems of algebraic equations are solved at each time step defined by the user.
The [Results] tab allows defining the result types displayable in the studies tree after finishing calculations.
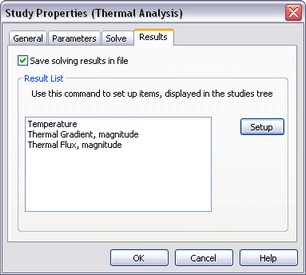
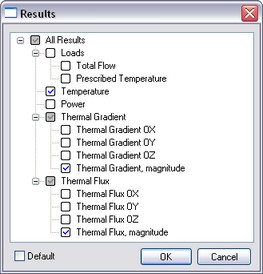
«Results» tab (left) and dialogue for setting results displayable by default in the studies tree (right)