 |
AutoFEM Analysis Acceleration | ||||||
To specify the load Acceleration, use one of the following methods:
Command Line: |
FEMAACCEL |
Main Menu: |
AutoFEM | Loads/Restraints | Acceleration |
Icon: |
|
Acceleration creates a uniform impact on any body with a mass. This impact is uniformly distributed over the entire volume of the selected body. Using of this type of loading allows, for example, simulating the load of the own weight under the force of gravity.
After invoking this command, it is necessary to select the body (or several bodies) for applying the load. You can select all bodies of the study at the same time by the menu option:
|
Select all bodies of the study |
They will be added to the list.
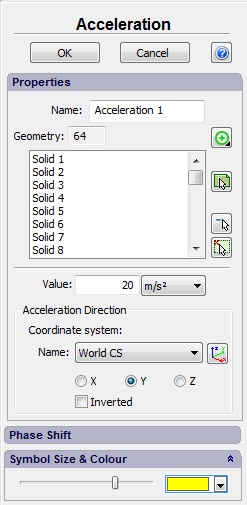
It is necessary to specify:
•magnitude of load;
•units: m/sec2, cm/sec2, in/sec2;
•load direction;
in the properties window.
Load direction. The user can select an axis (X,Y or Z) of the local coordinate system (if the local coordinate system is not specified, the global coordinate system will be used by default) as a direction of acceleration.
The user can tick the option "Inverted" to reverse the load direction.
In the 3D scene, the load Acceleration is shown in the following way:
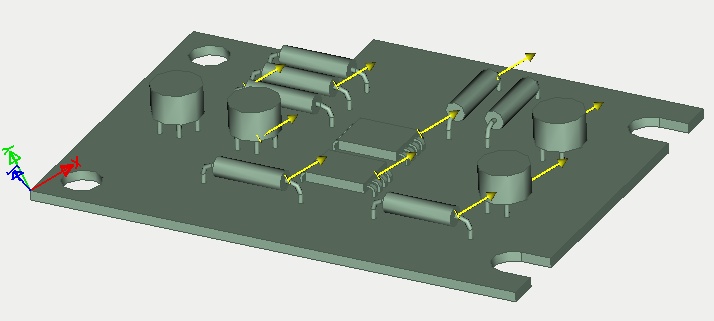
A typical sequence of steps to specify the load Acceleration:
1.Initiate command Acceleration ![]() .
.
2.Specify the units and value of acceleration.
3.Specify the direction of load.
4.Complete the command.
See also: Mechanical Loads, Force, Pressure, Hydrostatic Pressure, Centrifugal Force, Gravity, Acceleration, Bearing Load, Torque, Torque at Nodes, Additional Mass, Remote Force, Remote Moment, Remote Mass