 |
AutoFEM Analysis Remote Force | ||||||
The command permits one to assign a force action on a structure from any external object for which it is unreasonable (or impossible) for whatever reason to be included directly in the study. A classic example is the assessment of the resistance of a ship’s mast foundation to the wind load. In which case, an integral (aggregate) value of wind load and centre of application thereof is assigned.
Use the command to define a concentrated force and moment at a remote location. It is assumed, that the remote location is a location outside the model's geometry. The user should define the location and direction of force and moment in the specified coordinate system, and select geometric entities connected to the specified location. It is assumed, that the specified location is connected to the selected entities by virtual rigid bars. The selected entities (faces,edges, and vertices), being rigidly connected to a common point, can only deform as a rigid body. Therefore, high stresses can emerge near faces with rigid connections.
To specify the Remote Force, use one of the following methods:
Command Line: |
_FEMAREMFORCE |
Main Menu: |
AutoFEM | Loads/Restraints | Remote Loads | Remote Force |
Icon: |
|
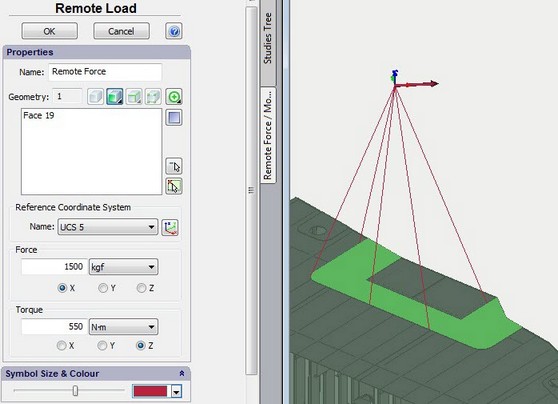
Typical sequence of steps for specifying the Remote Force:
1.Create a reference coordinate system in the point of a remote load application.
2.Initiate the command "Remote Force" ![]() .
.
3.Select a reference coordinate system to define the load location and direction.
4.Select a face, edge, vertex or a sequence of elements.
5.Specify the measurement units.
6.Specify the value of the load.
7.Complete the command.
See also: Mechanical Loads, Force, Pressure, Hydrostatic Pressure, Centrifugal Force, Gravity, Acceleration, Bearing Load, Torque, Torque at Nodes, Additional Mass, Remote Force, Remote Moment, Remote Mass